Theme 3.1: Structural characterization of molecules and supramolecular complexes
Structure & interaction studies
Objectives
- Establish molecular structure
- Understand molecular interactions
Summary
This theme deals with properties (structure, conformation, ionisation state) of drugs and other molecules of pharmaceutical interest (polymers, lipids, …) and aims at understanding of fundamental mechanisms of molecular interactions in various contexts (in pharmaceutical formulations, in nanostructures, in biological matrix, etc.).
To find these informations, we apply to complementary use of a range of analytical techniques, spectroscopic (Raman, surface-enhanced Raman – SERS, IR, fluorescence, UV-vis) and chromatographic (UHPLC SEC, UHPLC HIC, Capillary electrophoresis – CE).
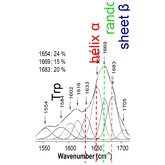
For instance, we have experience in protein structural analysis by Raman spectroscopy – this technique is able to provide the informations on the conformation, i.e. the ratio between alpha-helical, beta-sheet and random coil fractions of the amide bonds (Amide I zone located near 1650 cm-1) as well as the spatial conformation of the S-S bonds (band around 530 cm-1).
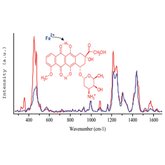
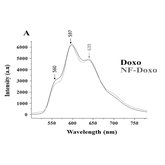
An other exemple is the molecular interactions of doxorubicine anticancer drug, within nanovectors where it is bound to the surface of iron oxide core (DOX-Fe2+ complex) or with autoassembled peptidic nanofibers. We have studied these interactions by means of SERS and fluorescence, respectively.
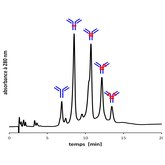
As for separation techniques, our expertise can be illustrated by characterization of an ADC (antibody-drug conjugate) in terms of DAR (drug/antibody ratio).
Some recent projects
Keywords
- Molecules & nanosystems characterization (conformation, structure)
- Drug-target interactions
- Raman/SERS/fluorescence confocal spectroscopy & imaging
- IR & UV-vis spectrophotometry
- (U)HPLC