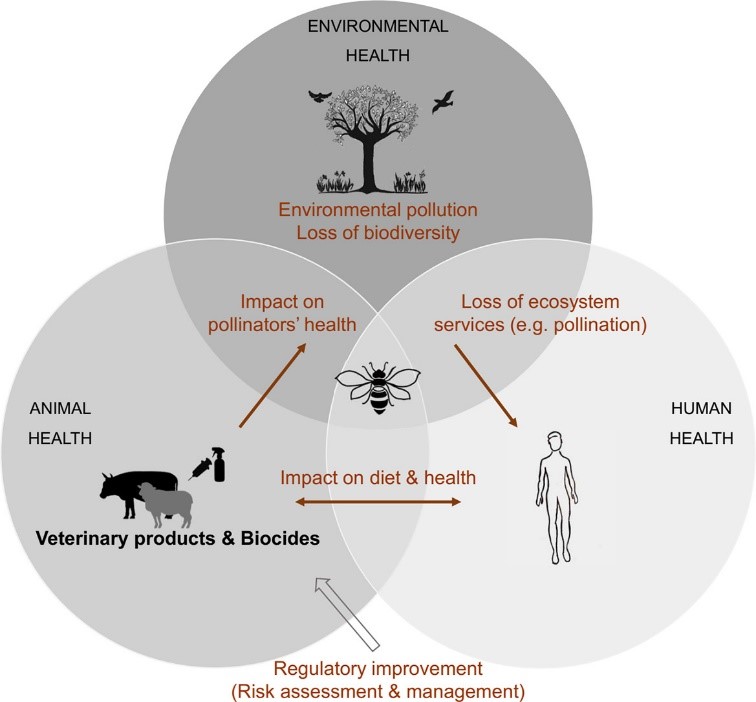
The “One Health” concept links environmental, animal (wild & livestock) and human health. It is increasingly being argued (e.g. Covid-19) and is now essential for the preservation of ecosystems and public health. Researchers from the universities of Leuven (BE), Sorbonne-CNRS-IRD-INRAE-UPEC (FR), CARI (BE), FNOSAD (FR) and the Centre for Molecular Biophysics (CNRS), have applied this concept to the case of biocides and veterinary products (including pesticides) that are used to treat livestock and that impact pollinators. These researchers have shown that these "multi-use substances" present (among other things) proven risks for bees and consequently need to be better assessed before being placed on the market. This work was initiated at the CBM in 2019: see here & here (Italian).
Reference : Mahefarisoa KL, Simon Delso N, Zaninotto V, Colin ME & Bonmatin JM (2021) The Threat of Veterinary Medicinal Products and Biocides on Pollinators: A One Health Perspective, One Health, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onehlt.2021.100237