A promising avenue for better crop protection and perhaps even for treating certain diseases, as reported by CNRS Chimie.
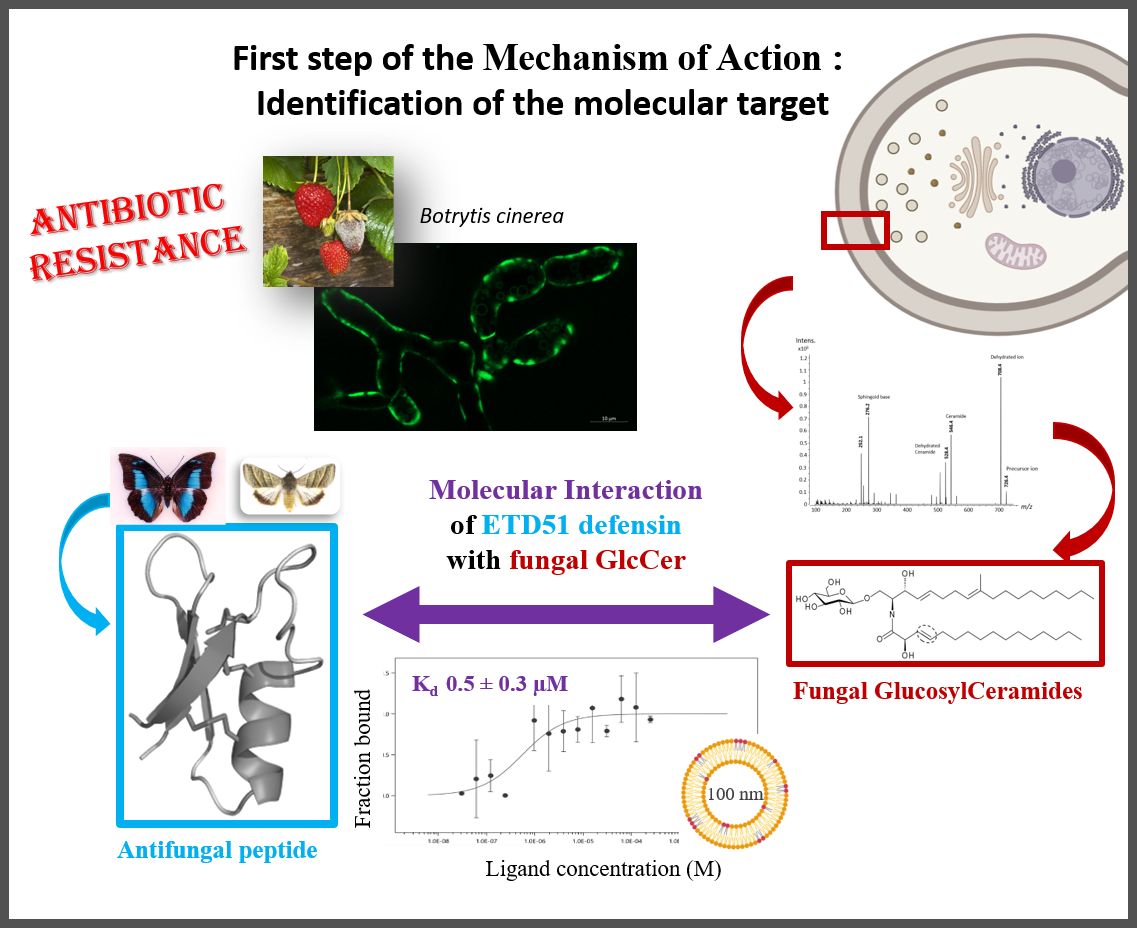
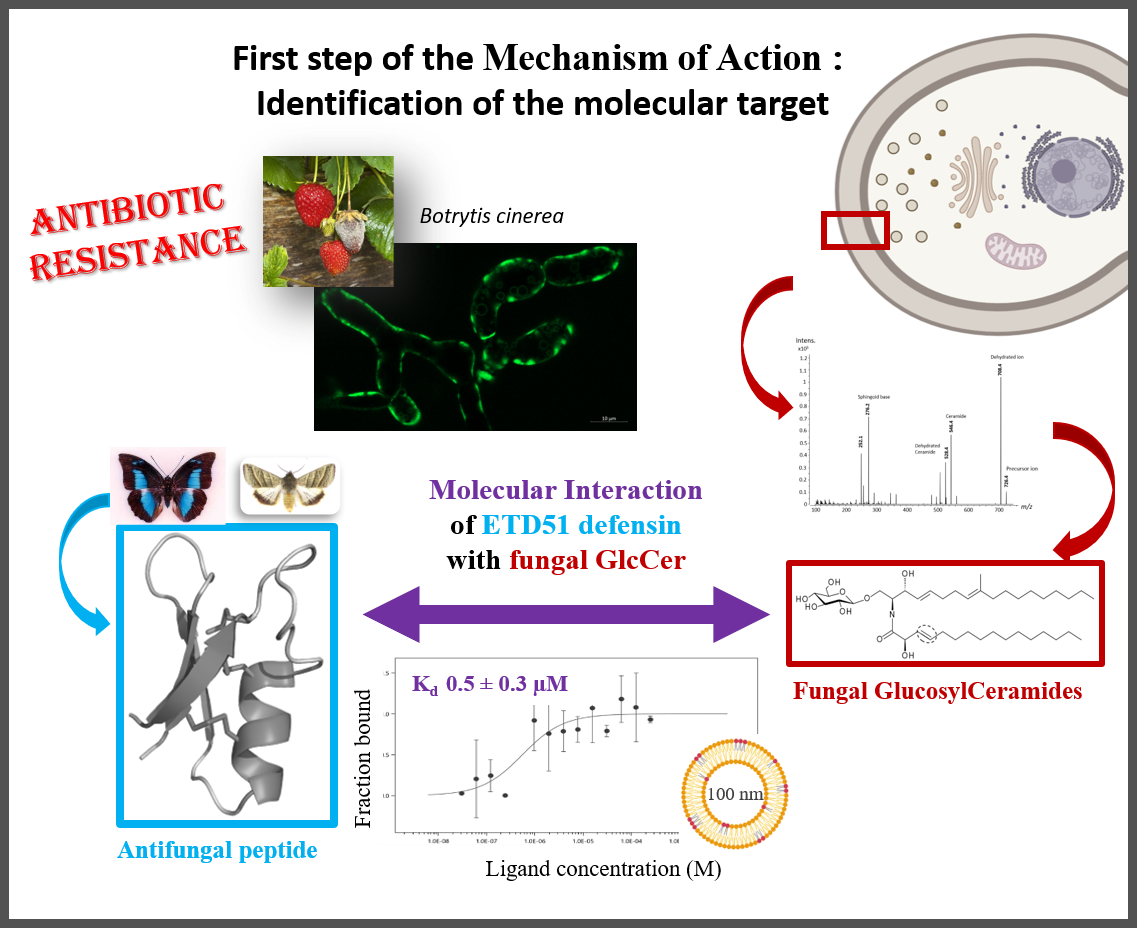
Fungal infections represent a major global health problem, with increasing resistance to currently available antifungal molecules. Targeting glucosylceramides (GlcCer), which are functionally essential glycosphingolipids present in fungal membranes, represents a promising strategy for the development of new antifungal agents.
GlcCer are associated with the antifungal activity of certain antimicrobial peptides found in plants and insects, known as defensins. The ETD151 peptide, optimised from butterfly defensins, is active against a range of fungal pathogens of interest to human health and agriculture. For example, the researchers have previously shown that ETD151 induces a multifaceted mechanism of action on Botrytis cinerea, a multi-resistant phytopathogenic fungus used here as a model (Aumer et al. 2020).
This multifaceted mechanism of action makes ETD151 a promising candidate for combating fungal resistance. The researchers took up the challenge of identifying its molecular target. They showed that the ETD151 peptide binds at the molecular level to GlcCer and localises preferentially to the membrane, where it induces various toxic effects. Identifying its molecular target and understanding the mode of action of ETD151 opens up new prospects for human health and crop protection.
Reference :
O. Kharrat, Y. Yamaryo-Botté, R. Nasreddine, S. Voisin, T. Aumer, B.P.A. Cammue, J. Madinier, T. Knobloch, K. Thevissen, R. Nehmé, V. Aucagne, C. Botté, P. Bulet, & C. Landon.
The antimicrobial activity of ETD151 defensin is dictated by the presence of glycosphingolipids in the targeted organisms.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (2025) 122 (7) e2415524122, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2415524122.