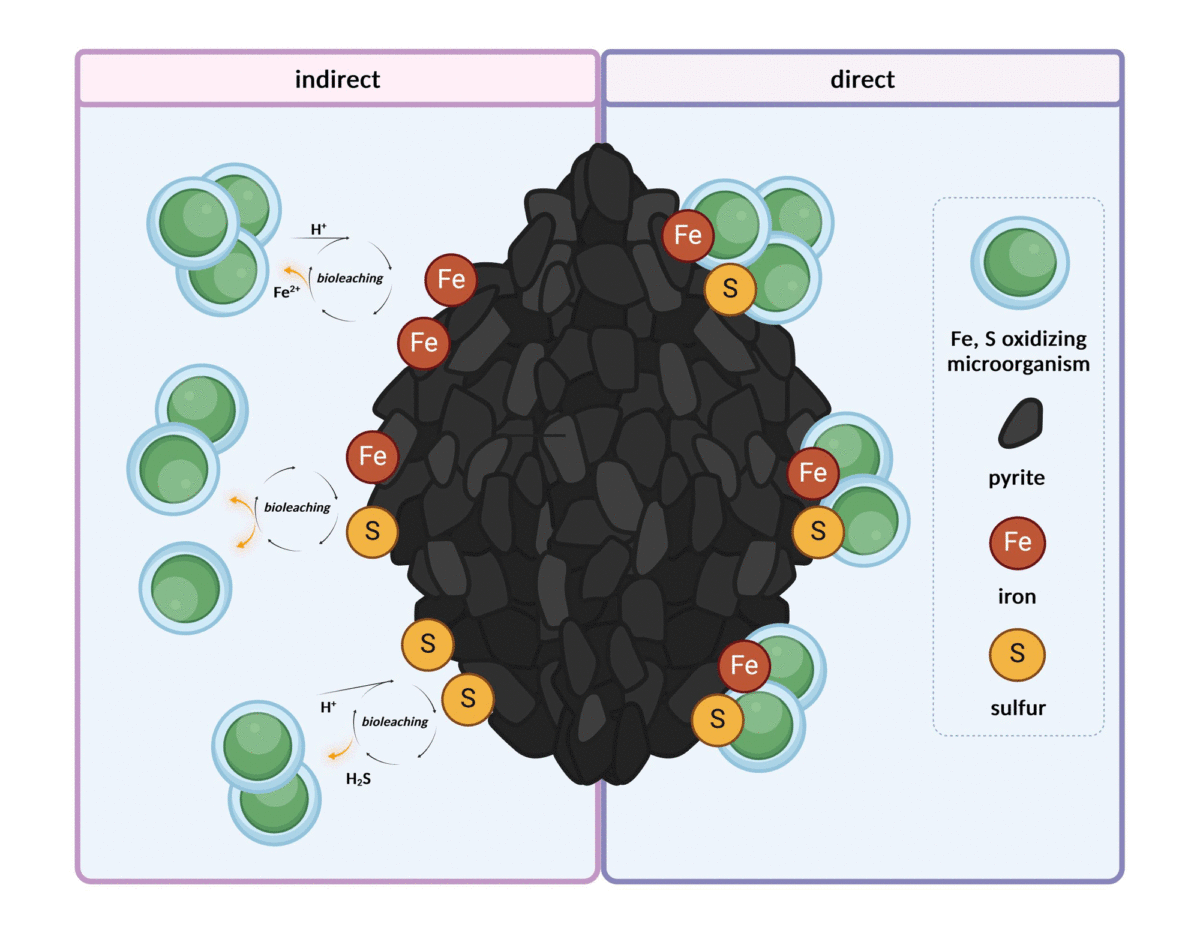
We investigated the metabolome of the iron- and sulfur-oxidizing, extremely thermoacidophilic archaeon Metallosphaera sedula grown on mineral pyrite (FeS2). The extraction of organic materials from these microorganisms is a major challenge because of the tight contact and interaction between cells and mineral materials. Therefore, we applied an improved protocol to break the microbial cells and separate their organic constituents from the mineral surface, to extract lipophilic compounds through liquid–liquid extraction, and performed metabolomics analyses using MALDI-TOF MS and UHPLC-UHR-Q/TOF. Using this approach, we identified several molecules involved in central carbon metabolism and in the modified Entner-Doudoroff pathway found in Archaea, sulfur metabolism-related compounds, and molecules involved in the adaptation of M. sedula to extreme environments, such as metal tolerance and acid resistance. Furthermore, we identified molecules involved in microbial interactions, i.e., cell surface interactions through biofilm formation and cell–cell interactions through quorum sensing, which relies on messenger molecules for microbial communication. Moreover, we successfully extracted and identified different saturated thiophene-bearing quinones using software for advanced compound identification (MetaboScape). These quinones are respiratory chain electron carriers in M. sedula, with biomarker potential for life detection in extreme environmental conditions.
Reference :
Gfellner SV, Colas C, Gabant G, Groninga J, Cadene M, Milojevic T. Improved protocol for metabolite extraction and identification of respiratory quinones in extremophilic Archaea grown on mineral materials. Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 8;15:1473270. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1473270