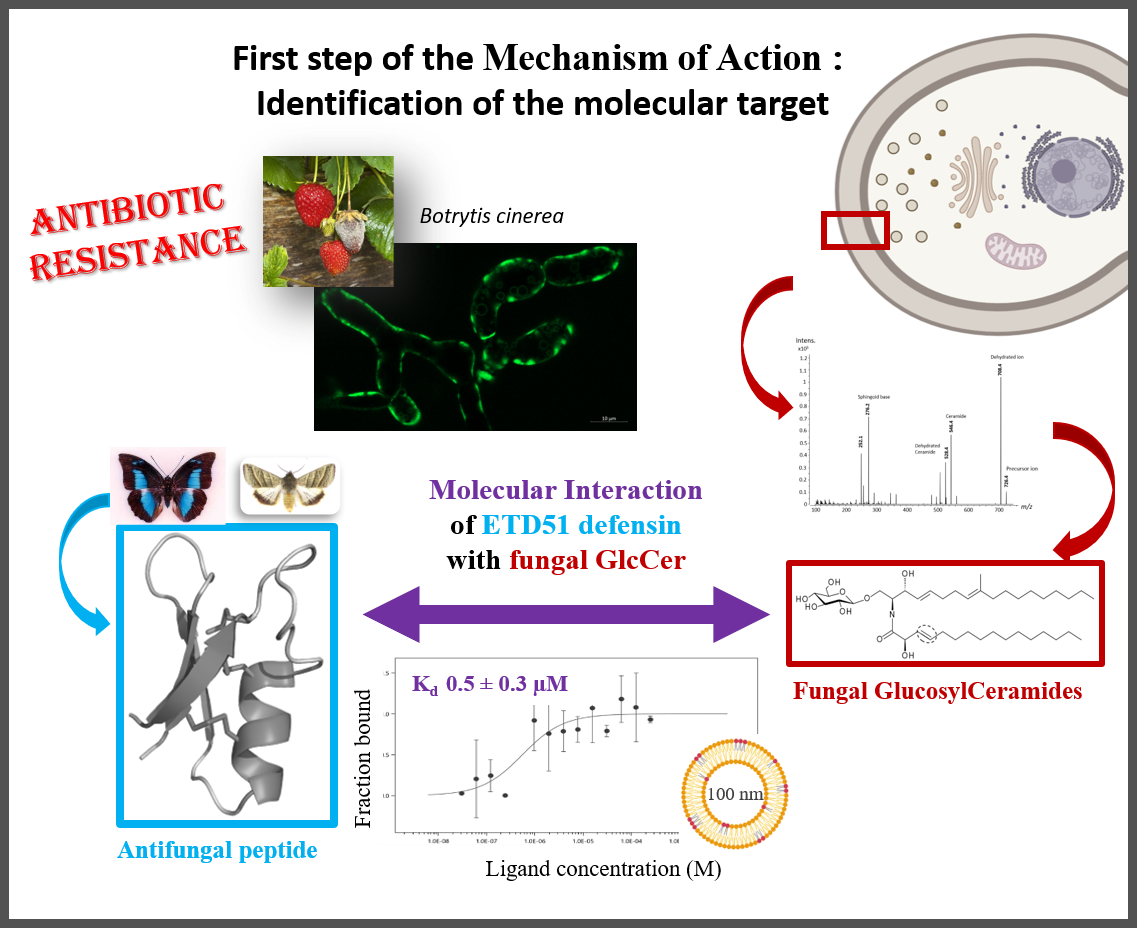
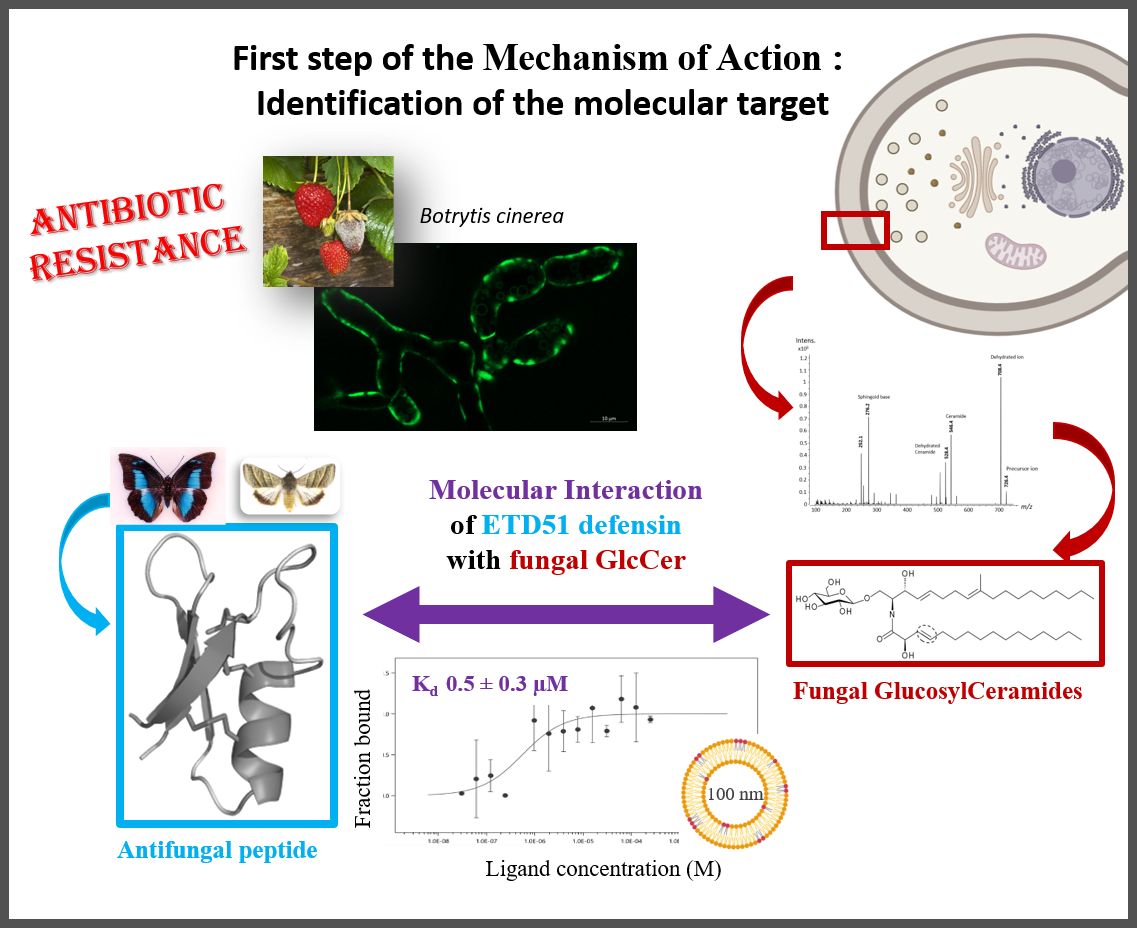
Fungal infections are a threat to human health and agriculture. It is therefore essential to develop new antifungal compounds with innovative mechanisms of action. Fungal glucosylceramides (GlcCer), which are essential for fungal pathogenicity, are a promising target.
The ETD151 peptide, optimized from butterfly defensins, acts against human fungal pathogens on the WHO priority list and plant pathogens such as B. cinerea used as a model. We recently showed that fungal GlcCers are the molecular target of the ETD151 peptide in the very first step of the mechanism of action (Kharrat et al PNAS 2025).
Through this study, which combines biophysical and spectroscopic methods, we reveal the key structural elements of the interaction between the ETD151 peptide and GlcCer at the molecular level. In particular, the presence of a methyl group specific to fungal GlcCer plays a role in the membrane disorder induced by the peptide and increases the binding affinity between the partners.
These results pave the way for the optimization and development of defensin mimics to selectively combat pathogenic fungi by targeting methylated GlcCer while minimizing toxicity to the host.
References:
Molecular recognition of fungal methylated glucosylceramides by ETD151 defensin.
Ons Kharrat, Françoise Paquet, Rouba Nasreddine, Jean-Baptiste Madinier, Reine Nehmé, Vincent Aucagne, Philippe Bulet, Dror Warschawski, and Céline Landon.
Journal of Biological Chemistry Volume 301, Issue 9, 110587
doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110587